SCIM Documentation
Your enterprise customers are asking:
- “Can we automatically provision users from our identity provider?”
- “Do you support SCIM for Okta/Entra?”
- “How do we deprovision employees when they leave?”
- “Can we sync user groups from our IdP?”
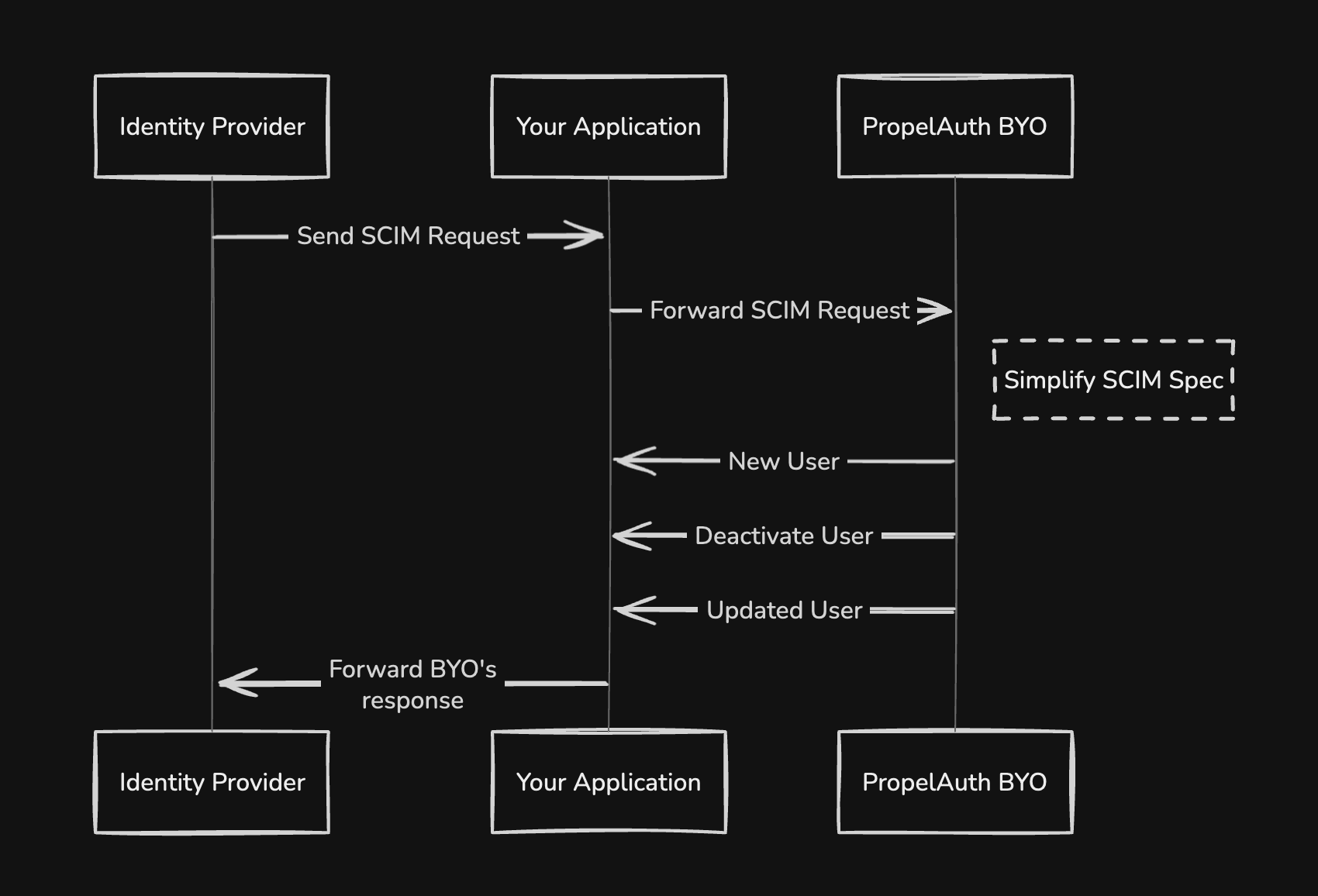
PropelAuth BYO SCIM lets you say “yes” to all of these. SCIM (System for Cross-domain Identity Management) automatically syncs users between your customers’ identity providers and your application - when someone joins their company, they’re added to your app; when they leave, they’re removed.
Building SCIM support from scratch means implementing a complex specification, handling provider variations, and maintaining multiple endpoints. With PropelAuth BYO, you build one endpoint that handles everything. We parse the SCIM requests, tell you what needs to happen (“create user john@acme.com”), and you just update your database.
By the end of this guide, you’ll have:
- One API endpoint that handles all SCIM operations
- Automatic user provisioning and deprovisioning
- Support for any SCIM-compliant identity provider
- Full control over how user data maps to your system
How SCIM Works with BYO
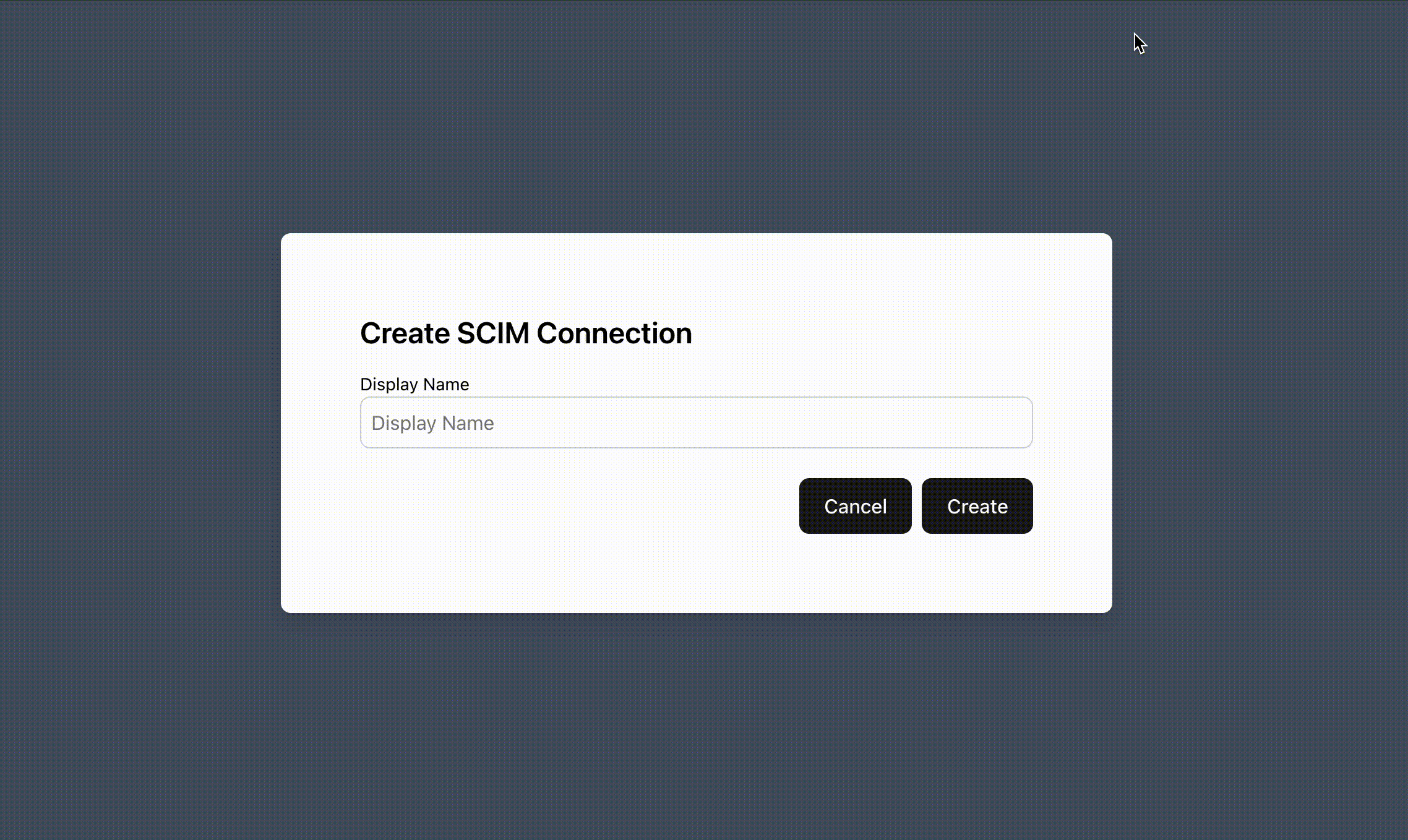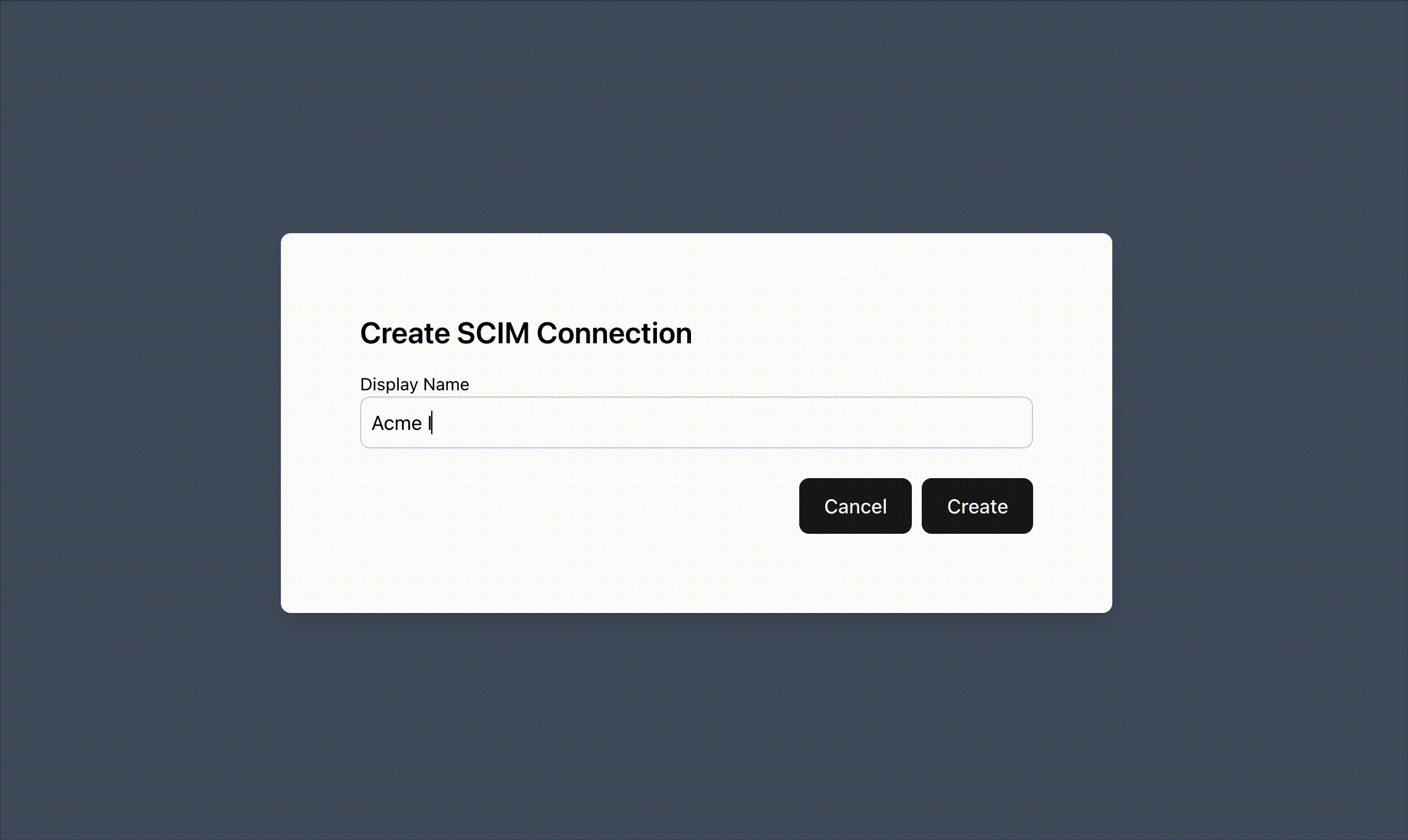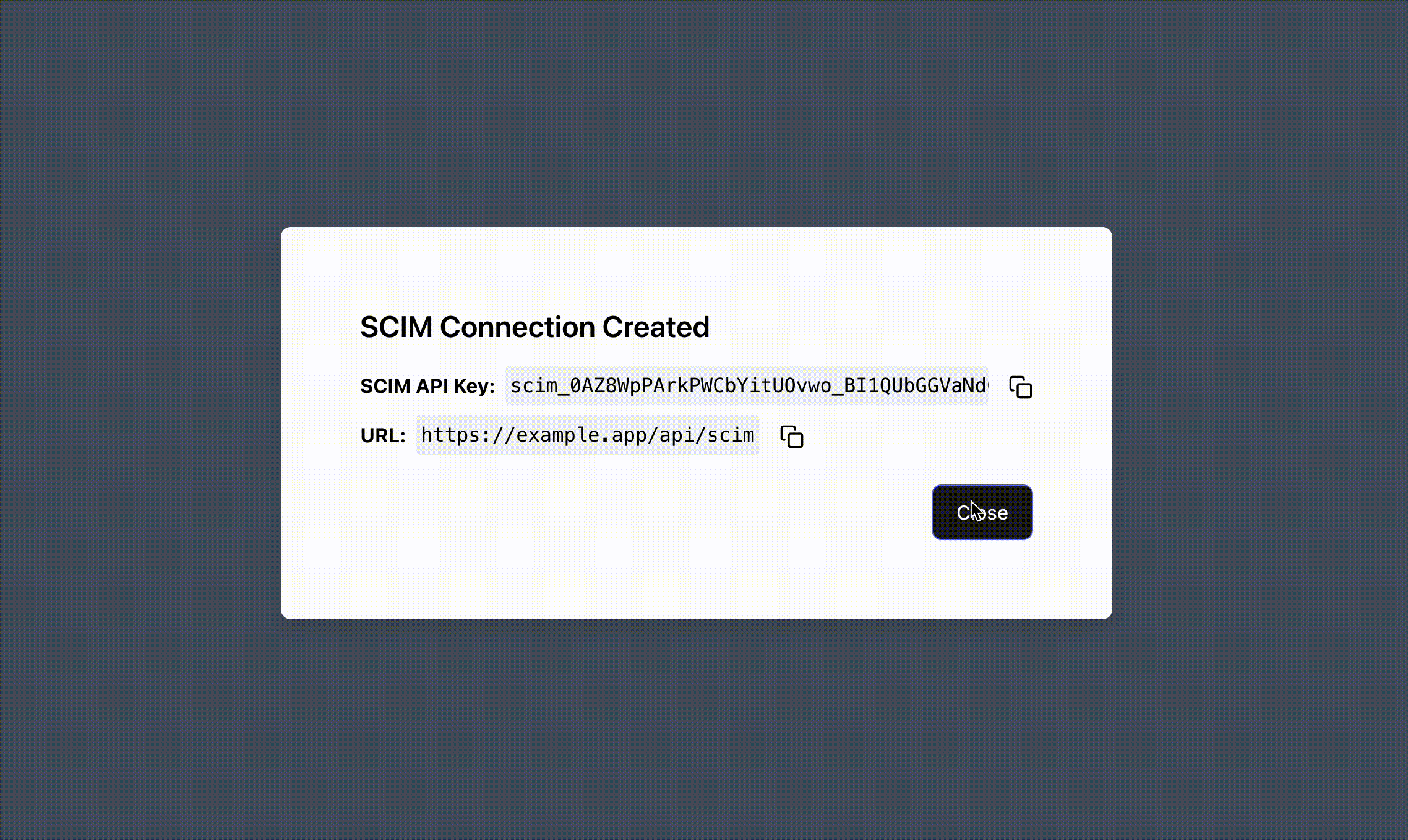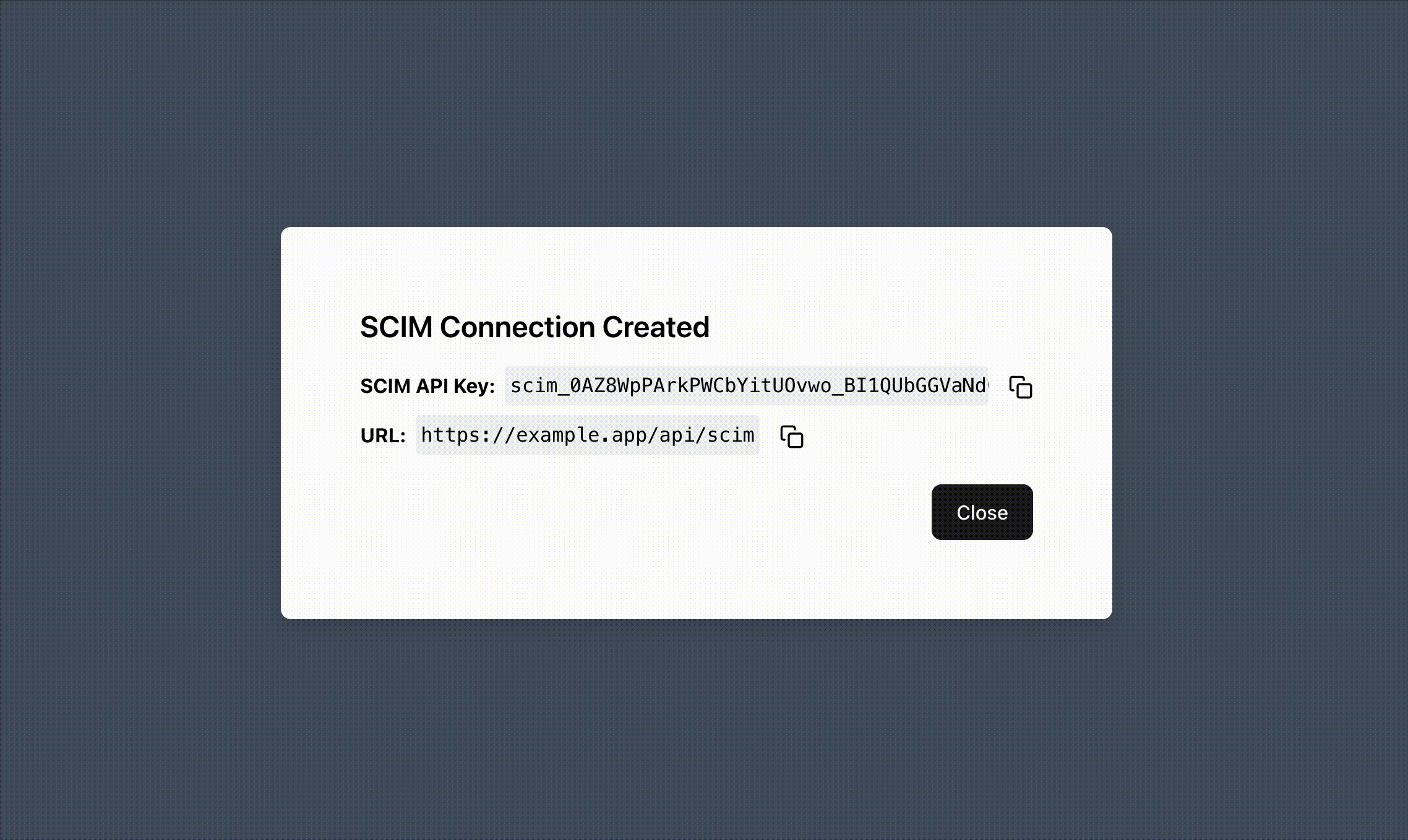
Section titled “How SCIM Works with BYO”When your customers start the process of integrating your app with their SCIM IdP, they typically expect two variables - a SCIM API Key and a SCIM URL. The SCIM URL is up to you (see here for more information), and the SCIM API Key can be generated by creating a SCIM Connection via the Create SCIM Session function.
// Endpoint for customers to set up SCIMapp.post("/api/admin/scim/setup", async (req, res) => { // Get the organization ID (your logic) const organizationId = getOrganizationIdFromRequest(req);
// Create a new SCIM connection for this customer const result = await auth.scim.management.createScimConnection({ customerId: organizationId, });
if (result.ok) { // These are the two values your customer needs: const scimApiKey = result.data.scimApiKey; const scimBaseUrl = "https://your-app.com/api/scim";
res.json({ scimApiKey, scimBaseUrl, message: "Provide these to your identity provider" }); } else { console.error("Failed to create SCIM connection:", result.error); res.status(500).json({ error: "Failed to create SCIM connection" }); }});# Endpoint for customers to set up SCIM@app.post("/api/admin/scim/setup")async def setup_scim(request: Request): # Get the organization ID (your logic) organization_id = get_organization_id_from_request(request)
# Create a new SCIM connection for this customer result = await client.scim.management.create_scim_connection( customer_id=organization_id, )
if is_ok(result): # These are the two values your customer needs: scim_api_key = result.data.scim_api_key scim_base_url = "https://your-app.com/api/scim"
return { "scimApiKey": scim_api_key, "scimBaseUrl": scim_base_url, "message": "Provide these to your identity provider" } else: print("Failed to create SCIM connection:", result.error) raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Failed to create SCIM connection")// Endpoint for customers to set up SCIM@PostMapping("/api/admin/scim/setup")public ResponseEntity<?> setupScim(HttpServletRequest request) { // Get the organization ID (your logic) String organizationId = getOrganizationIdFromRequest(request);
// Create a new SCIM connection for this customer CreateScimConnectionResponse result = propelAuthClient.scim.management.createScimConnection( CreateScimConnectionCommand.builder() .customerId(organizationId) .build() );
// These are the two values your customer needs: String scimApiKey = result.getScimApiKey(); String scimBaseUrl = "https://your-app.com/api/scim";
return ResponseEntity.ok(Map.of( "scimApiKey", scimApiKey, "scimBaseUrl", scimBaseUrl, "message", "Provide these to your identity provider" ));}// Endpoint for customers to set up SCIMapp.MapPost("/api/admin/scim/setup", async (HttpContext context) =>{ // Get the organization ID (your logic) var organizationId = GetOrganizationIdFromRequest(context);
// Create a new SCIM connection for this customer var result = await propelAuthClient.Scim.Management.CreateScimConnectionAsync( new CreateScimConnectionCommand { CustomerId = organizationId } );
// These are the two values your customer needs: var scimApiKey = result.ScimApiKey; var scimBaseUrl = "https://your-app.com/api/scim";
return Results.Ok(new { ScimApiKey = scimApiKey, ScimBaseUrl = scimBaseUrl, Message = "Provide these to your identity provider" });});SCIM works by having identity providers (IdPs) send standardized HTTP requests to specific endpoints on the target application, such as POST to /Users to create a new user or PUT to /Users/{userId} to update an existing user’s attributes. The application must implement these SCIM API endpoints to receive and process the JSON payloads containing user and group data, then translate that information into its own internal user management system.
BYO SCIM functions handle these requests for you, lets you know if you need to take an action from those requests, and then builds a response that you can send back to the IdP.
Instead of creating and managing multiple API endpoints to handle these requests, you can simply create one wildcard API to handle all requests from each of your SCIM connections.
// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operationsapp.use("/api/scim", async (req, res) => { // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO const result = await auth.scim.scimRequest({ method: req.method, pathAndQueryParams: req.url, body: req.body, scimApiKey: req.headers.authorization, });
if (!result.ok) { console.error("SCIM request failed:", result.error); return res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal error" }); }
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result.data.status === "ActionRequired") { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP res.status(result.data.responseHttpCode).json(result.data.responseData);});# One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operations@app.api_route("/api/scim/{path:path}", methods=["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"])async def scim_handler(request: Request): body = await request.json() if request.method in ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH"] else None
result = await client.scim.scim_request( method=request.method, path_and_query_params=str(request.url.path) + ("?" + str(request.url.query) if request.url.query else ""), body=body, scim_api_key=request.headers.get("authorization"), )
if is_err(result): print("SCIM request failed:", result.error) raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Internal error")
# Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if result.data.status == "ActionRequired": # Handle the required action (see below for details) # ... pass
return JSONResponse( status_code=result.data.response_http_code, content=result.data.response_data )// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operations@RequestMapping("/api/scim/**")public ResponseEntity<?> scimHandler(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody(required = false) Map<String, Object> body) { // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO String pathAndQueryParams = request.getRequestURI(); if (request.getQueryString() != null) { pathAndQueryParams += "?" + request.getQueryString(); }
ScimRequestResponse result = propelAuthClient.scim.scimRequest( ScimRequestCommand.builder() .method(HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethod().toUpperCase())) .pathAndQueryParams(pathAndQueryParams) .body(JsonValue.of(body)) .scimApiKey(request.getHeader("Authorization")) .build() );
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result instanceof ScimRequestResponse.ActionRequired) { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP ScimRequestResponse.Completed completed = (ScimRequestResponse.Completed) result; return ResponseEntity.status(completed.getResponseHttpCode()).body(completed.getResponseData());}// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operationsapp.Map("/api/scim/{*path}", async (HttpContext context) =>{ // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO var requestBody = await new StreamReader(context.Request.Body).ReadToEndAsync(); var result = await propelAuthClient.Scim.ScimRequestAsync(new ScimRequestCommand { Method = Enum.Parse<HttpMethod>(context.Request.Method, ignoreCase: true), PathAndQueryParams = context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString, Body = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(requestBody) ? null : JsonSerializer.Deserialize<JsonElement>(requestBody), ScimApiKey = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString(), });
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result is not ScimRequestResponseCompleted) { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP var completed = (ScimRequestResponseCompleted)result; context.Response.StatusCode = completed.ResponseHttpCode; await context.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(completed.ResponseData);});Creating SCIM Connections
Section titled “Creating SCIM Connections”Adding SCIM support begins with creating a SCIM Connection via the Create SCIM Session function. Typically, a group of users that logs in together such as organizations, groups, tenants, etc will share a SCIM Connection. However, if a group of users want to use multiple IdPs for SCIM, one SCIM Connection should be created per each of their IdPs.
The Create SCIM Connection function returns a SCIM API Key that your users can input into their SCIM IdP.
There are several arguments that can be used when creating a SCIM Connection.
-
Display Name: This can be used as a customer facing identifier for the SCIM Connection. It will be returned when using the Fetch SCIM Connection function.
-
SCIM API Key Expiration: A UNIX timestamp of when the SCIM API Key will expire. If this argument is not included the SCIM API Key will be set to never expire. If you do include an expiration, make sure to alert your customers when they’ll need to update their SCIM API Key. Use the Reset SCIM Connection API Key function to create a new API Key for a SCIM connection.
-
Customer ID: Can be used to link a SCIM Connection to a group of users, such as an organization, group, or tenant. When you include this field you can use it to fetch the SCIM connection.
-
Custom Mapping: An easy way to get a standardized schema from SCIM connections. The custom mapping includes what fields you expect to be sent via SCIM and where to find them. This will most commonly be used to assist with small differences between SCIM providers, so you don’t need to write custom code for each customer. The default property mapping will be used if this field is not included. See here for more information.
One SCIM Route to Rule Them All
Section titled “One SCIM Route to Rule Them All”Here’s the magic: instead of building 10+ different endpoints to support SCIM, you build just one. Traditional SCIM implementations require you to build and manage multiple APIs to communicate with your customer’s SCIM providers. For example:
GET /Users: Returns all users of a SCIM connection as well as support for query parameters to filter for users based on email, username, and more.GET /Users/{userId}: Returns a user based on user ID.POST /Users: Creates a user.GET /Groups: Returns all groups of a SCIM connection as well as support for query parameters to filter based on group name.GET /Groups/{groupId}: Returns a group based on group ID.POST /Groups: Creates a group
And that’s not even all of them! But don’t fret, with our SCIM BYO functions you only need to build one route, that’s it. Instead of building multiple endpoints, simply create a catch all that accepts all HTTP Methods. For each request that hits that route you’ll need to provide the HTTP Method, URL path and query parameters, the request body, and the SCIM API Key.
// Captures ALL SCIM requests: GET /Users, POST /Groups, etc.app.use("/api/scim", async (req, res) => { // Extract the values BYO needs: const httpMethod = req.method; // "GET", "POST", "DELETE", etc. const pathAndParams = req.url; // "/Users?filter=email+eq+\"john@example.com\"" const requestBody = req.body; // The SCIM payload (if any) const apiKey = req.headers.authorization; // Bearer token from the IdP
// Pass everything to BYO's SCIM handler // (see next example for complete implementation)});# Captures ALL SCIM requests: GET /Users, POST /Groups, etc.@app.api_route("/api/scim/{path:path}", methods=["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"])async def scim_handler(request: Request, path: str): # Extract the values BYO needs: http_method = request.method # "GET", "POST", "DELETE", etc. path_and_params = "/" + path + ("?" + request.url.query if request.url.query else "") # "/Users?filter=email+eq+\"john@example.com\"" request_body = await request.json() if request.method in ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH"] else None # The SCIM payload (if any) api_key = request.headers.get("authorization") # Bearer token from the IdP
# Pass everything to BYO's SCIM handler # (see next example for complete implementation)// Captures ALL SCIM requests: GET /Users, POST /Groups, etc.@RequestMapping("/api/scim/**")public ResponseEntity<?> scimHandler(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody(required = false) Map<String, Object> body) { // Extract the values BYO needs: String httpMethod = request.getMethod(); // "GET", "POST", "DELETE", etc. String pathAndParams = request.getRequestURI(); if (request.getQueryString() != null) { pathAndParams += "?" + request.getQueryString(); // "/Users?filter=email+eq+\"john@example.com\"" } Map<String, Object> requestBody = body; // The SCIM payload (if any) String apiKey = request.getHeader("Authorization"); // Bearer token from the IdP
// Pass everything to BYO's SCIM handler // (see next example for complete implementation)}// Captures ALL SCIM requests: GET /Users, POST /Groups, etc.app.Map("/api/scim/{*path}", async (HttpContext context) =>{ // Extract the values BYO needs: var httpMethod = context.Request.Method; // "GET", "POST", "DELETE", etc. var pathAndParams = context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString; // "/Users?filter=email+eq+\"john@example.com\"" var requestBody = await new StreamReader(context.Request.Body).ReadToEndAsync(); // The SCIM payload (if any) var apiKey = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString(); // Bearer token from the IdP
// Pass everything to BYO's SCIM handler // (see next example for complete implementation)});Forward these values to the SCIM Request function and it will process the request, let you know if any actions need to be taken on your end, and provide you with a response body and status.
// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operationsapp.use("/api/scim", async (req, res) => { // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO const result = await auth.scim.scimRequest({ method: req.method, pathAndQueryParams: req.url, body: req.body, scimApiKey: req.headers.authorization, });
if (!result.ok) { console.error("SCIM request failed:", result.error); return res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal error" }); }
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result.data.status === "ActionRequired") { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP res.status(result.data.responseHttpCode).json(result.data.responseData);});# One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operations@app.api_route("/api/scim/{path:path}", methods=["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"])async def scim_handler(request: Request): body = await request.json() if request.method in ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH"] else None
result = await client.scim.scim_request( method=request.method, path_and_query_params=str(request.url.path) + ("?" + str(request.url.query) if request.url.query else ""), body=body, scim_api_key=request.headers.get("authorization"), )
if is_err(result): print("SCIM request failed:", result.error) raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Internal error")
# Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if result.data.status == "ActionRequired": # Handle the required action (see below for details) # ... pass
return JSONResponse( status_code=result.data.response_http_code, content=result.data.response_data )// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operations@RequestMapping("/api/scim/**")public ResponseEntity<?> scimHandler(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody(required = false) Map<String, Object> body) { // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO String pathAndQueryParams = request.getRequestURI(); if (request.getQueryString() != null) { pathAndQueryParams += "?" + request.getQueryString(); }
ScimRequestResponse result = propelAuthClient.scim.scimRequest( ScimRequestCommand.builder() .method(HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethod().toUpperCase())) .pathAndQueryParams(pathAndQueryParams) .body(JsonValue.of(body)) .scimApiKey(request.getHeader("Authorization")) .build() );
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result instanceof ScimRequestResponse.ActionRequired) { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP ScimRequestResponse.Completed completed = (ScimRequestResponse.Completed) result; return ResponseEntity.status(completed.getResponseHttpCode()).body(completed.getResponseData());}// One endpoint handles ALL SCIM operationsapp.Map("/api/scim/{*path}", async (HttpContext context) =>{ // Pass the request to PropelAuth BYO var requestBody = await new StreamReader(context.Request.Body).ReadToEndAsync(); var result = await propelAuthClient.Scim.ScimRequestAsync(new ScimRequestCommand { Method = Enum.Parse<HttpMethod>(context.Request.Method, ignoreCase: true), PathAndQueryParams = context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString, Body = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(requestBody) ? null : JsonSerializer.Deserialize<JsonElement>(requestBody), ScimApiKey = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString(), });
// Check if you need to take action (e.g., create/update user) if (result is not ScimRequestResponseCompleted) { // Handle the required action (see below for details) // ... }
// Send BYO's response back to the IdP var completed = (ScimRequestResponseCompleted)result; context.Response.StatusCode = completed.ResponseHttpCode; await context.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(completed.ResponseData);});That’s your entire SCIM implementation. PropelAuth BYO handles the SCIM specification complexity, and you just handle the business logic.
Handling Required Actions
Section titled “Handling Required Actions”Some SCIM requests will require you to take action on your end, such as creating a new user in your database or disabling a user when they are deprovisioned.
When an important change is detected by the SCIM Request function it will not return a SCIM response and instead return an Action Required status. When this status is returned it will include information about the user as well as a Commit ID and Action Type.
You should handle the action appropriately based on the action type and then confirm the change with either the Link SCIM User or Commit SCIM User Change functions. Both of these functions will provide you with a SCIM response body and status that you can send back to the IdP.
Action Types
Section titled “Action Types”The SCIM Request function will alert you of important changes to your users and groups via Action Types. There are four action types and you should handle each one appropriately before confirming the change with the correct function.
-
Link User: Occurs when a new SCIM user is created. You can use the information provided about the user to create them in your database (or update them if they already exist). You then call the Link SCIM User function with YOUR user ID. The result is that we will always use your user ID as the primary identifier for that user going forward. This can also be useful if you want to do any additional setup for new users, such as sending a welcome email or setting up default permissions.
-
Disable User: Occurs when a user is set to inactive in your customer’s IdP (meaning they are no longer provisioned to your application). The user should no longer be able to log into your app when this change occurs and should be logged out as soon as possible. Confirm with the Commit SCIM User Change function.
-
Enable User: Occurs when an existing, previously inactive user is reprovisioned to your application, setting their status to active. This user should now be able to log into your app. Confirm with the Commit SCIM User Change function.
-
Delete User: Occurs when a user is deleted from the SCIM provider. The user should no longer be able to log into your app when this change occurs and should be logged out as soon as possible. Confirm with the Commit SCIM User Change function. Unlike Disable User, this action is not reversible.
// Your SCIM endpointapp.use("/api/scim", async (req, res) => { const result = await auth.scim.scimRequest({ method: req.method, pathAndQueryParams: req.url, body: req.body, scimApiKey: req.headers.authorization, });
if (!result.ok) { console.error("SCIM request failed:", result.error); return res.status(500).json({ error: "Internal error" }); }
// Handle any required actions if (result.data.status === "ActionRequired") { const response = await handleRequiredScimAction(result.data); return res.status(response.data.responseHttpCode).json(response.data.responseData); }
// No action needed - return BYO's response res.status(result.data.responseHttpCode).json(result.data.responseData);});
// Handle the 4 SCIM actions you need to implementasync function handleRequiredScimAction(data) { const { action, connectionId, commitId } = data;
if (action === "LinkUser") { // New user from IdP - create or link to existing const userId = await lookupOrCreateScimUser({ primaryEmail: data.primaryEmail, userName: data.userName, active: data.active, customData: data.parsedUserData, });
return await auth.scim.linkScimUser({ connectionId, commitId, userId, }); }
if (action === "DeleteUser") { // User removed from IdP await deleteUser(data.userId); } else if (action === "DisableUser") { // User deprovisioned await setUserActive(data.userId, false); } else if (action === "EnableUser") { // User reprovisioned await setUserActive(data.userId, true); }
// Confirm the action was handled return await auth.scim.commitScimUserChange({ connectionId, commitId, });}# Your SCIM endpoint@app.api_route("/api/scim/{path:path}", methods=["GET", "POST", "PUT", "PATCH", "DELETE"])async def scim_handler(request: Request): body = await request.json() if request.method in ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH"] else None
result = await client.scim.scim_request( method=request.method, path_and_query_params=str(request.url.path) + ("?" + str(request.url.query) if request.url.query else ""), body=body, scim_api_key=request.headers.get("authorization"), )
if is_err(result): print("SCIM request failed:", result.error) raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail="Internal error")
# Handle any required actions if result.data.status == "ActionRequired": response = await handle_required_scim_action(result.data) return JSONResponse( status_code=response.data.response_http_code, content=response.data.response_data )
# No action needed - return BYO's response return JSONResponse( status_code=result.data.response_http_code, content=result.data.response_data )
# Handle the 4 SCIM actions you need to implementasync def handle_required_scim_action(data): connection_id = data.connection_id commit_id = data.commit_id
if data.action == "LinkUser": # New user from IdP - create or link to existing user_id = await lookup_or_create_scim_user( email=data.primary_email, user_name=data.user_name, active=data.active, custom_data=data.parsed_user_data, )
return await client.scim.link_scim_user( connection_id=connection_id, commit_id=commit_id, user_id=user_id, )
if data.action == "DeleteUser": # User removed from IdP await delete_user(data.user_id) elif data.action == "DisableUser": # User deprovisioned await set_user_active(data.user_id, False) elif data.action == "EnableUser": # User reprovisioned await set_user_active(data.user_id, True)
# Confirm the action was handled return await client.scim.commit_scim_user_change( connection_id=connection_id, commit_id=commit_id, )// Your SCIM endpoint@RequestMapping("/api/scim/**")public ResponseEntity<?> scimHandler(HttpServletRequest request, @RequestBody(required = false) Map<String, Object> body) { String pathAndQueryParams = request.getRequestURI(); if (request.getQueryString() != null) { pathAndQueryParams += "?" + request.getQueryString(); }
ScimRequestResponse result = propelAuthClient.scim.scimRequest( ScimRequestCommand.builder() .method(HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethod().toUpperCase())) .pathAndQueryParams(pathAndQueryParams) .body(JsonValue.of(body)) .scimApiKey(request.getHeader("Authorization")) .build() );
// Handle any required actions if (result instanceof ScimRequestResponse.ActionRequired) { CompletedScimRequestResponse response = handleRequiredScimAction((ScimRequestResponse.ActionRequired) result); return ResponseEntity.status(response.getResponseHttpCode()).body(response.getResponseData()); }
// No action needed - return BYO's response ScimRequestResponse.Completed completed = (ScimRequestResponse.Completed) result; return ResponseEntity.status(completed.getResponseHttpCode()).body(completed.getResponseData());}
// Handle the 4 SCIM actions you need to implementprivate CompletedScimRequestResponse handleRequiredScimAction(ScimRequestResponse.ActionRequired action) { String connectionId = action.getConnectionId(); String commitId = action.getCommitId();
if (action instanceof ActionRequiredLinkUser) { ActionRequiredLinkUser linkUser = (ActionRequiredLinkUser) action; // New user from IdP - create or link to existing String userId = lookupOrCreateScimUser( linkUser.getPrimaryEmail(), linkUser.getUserName(), linkUser.getActive(), linkUser.getParsedUserData() );
return propelAuthClient.scim.linkScimUser( LinkScimUserCommand.builder() .connectionId(connectionId) .commitId(commitId) .userId(userId) .build() ); }
if (action instanceof ActionRequiredDeleteUser) { // User removed from IdP deleteUser(((ActionRequiredDeleteUser) action).getUserId()); } else if (action instanceof ActionRequiredDisableUser) { // User deprovisioned setUserActive(((ActionRequiredDisableUser) action).getUserId(), false); } else if (action instanceof ActionRequiredEnableUser) { // User reprovisioned setUserActive(((ActionRequiredEnableUser) action).getUserId(), true); }
// Confirm the action was handled return propelAuthClient.scim.commitScimUserChange( CommitScimUserChangeCommand.builder() .connectionId(connectionId) .commitId(commitId) .build() );}// Your SCIM endpointapp.Map("/api/scim/{*path}", async (HttpContext context) =>{ var requestBody = await new StreamReader(context.Request.Body).ReadToEndAsync(); var result = await propelAuthClient.Scim.ScimRequestAsync(new ScimRequestCommand { Method = Enum.Parse<HttpMethod>(context.Request.Method, ignoreCase: true), PathAndQueryParams = context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString, Body = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(requestBody) ? null : JsonSerializer.Deserialize<JsonElement>(requestBody), ScimApiKey = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString(), });
// Handle any required actions if (result is not ScimRequestResponseCompleted) { var response = await HandleRequiredScimAction(result); context.Response.StatusCode = response.ResponseHttpCode; await context.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(response.ResponseData); return; }
// No action needed - return BYO's response var completed = (ScimRequestResponseCompleted)result; context.Response.StatusCode = completed.ResponseHttpCode; await context.Response.WriteAsJsonAsync(completed.ResponseData);});
// Handle the 4 SCIM actions you need to implementasync Task<CompletedScimRequestResponse> HandleRequiredScimAction(ScimRequestResponse action){ var connectionId = action switch { ActionRequired.LinkUser l => l.ConnectionId, ActionRequired.DeleteUser d => d.ConnectionId, ActionRequired.DisableUser d => d.ConnectionId, ActionRequired.EnableUser e => e.ConnectionId, _ => throw new Exception("Unknown action type") };
var commitId = action switch { ActionRequired.LinkUser l => l.CommitId, ActionRequired.DeleteUser d => d.CommitId, ActionRequired.DisableUser d => d.CommitId, ActionRequired.EnableUser e => e.CommitId, _ => throw new Exception("Unknown action type") };
if (action is ActionRequired.LinkUser linkUser) { // New user from IdP - create or link to existing var userId = await LookupOrCreateScimUser( linkUser.PrimaryEmail, linkUser.UserName, linkUser.Active, linkUser.ParsedUserData );
return await propelAuthClient.Scim.LinkScimUserAsync(new LinkScimUserCommand { ConnectionId = connectionId, CommitId = commitId, UserId = userId }); }
if (action is ActionRequired.DeleteUser deleteUser) { // User removed from IdP await DeleteUser(deleteUser.UserId); } else if (action is ActionRequired.DisableUser disableUser) { // User deprovisioned await SetUserActive(disableUser.UserId, false); } else if (action is ActionRequired.EnableUser enableUser) { // User reprovisioned await SetUserActive(enableUser.UserId, true); }
// Confirm the action was handled return await propelAuthClient.Scim.CommitScimUserChangeAsync(new CommitScimUserChangeCommand { ConnectionId = connectionId, CommitId = commitId });}Updating Your User Data
Section titled “Updating Your User Data”While the SCIM Request function will require you to acknowledge any critical changes that occur, such as a new user getting created, it is less opinionated with non-critical changes. A common example of this is the user’s first and last names - while not critical, not updating these variables can cause a poor user experience in your app.
These requests will instead return a list of affectedUserIds, so you can decide how and when to update your user data.
You can use the Get SCIM User function to fetch the latest user information that the SCIM provider sent us, and you can either do this live whenever you need to load the user, periodically in the background, or before returning the SCIM response:
// After handling actions, sync any updated usersconst result = await auth.scim.scimRequest({ method: req.method, pathAndQueryParams: req.url, body: req.body, scimApiKey: req.headers.authorization,});
if (result.ok && result.data.status === "Completed") { // Sync any users that were modified // This isn't necessary, you can call getScimUser on demand as it's pretty fast for (const userId of result.data.affectedUserIds) { const userResult = await auth.scim.getScimUser({ scimConnectionId: result.data.connectionId, userId: userId, });
if (userResult.ok) { // Update your database with the latest SCIM data await updateUser(userId, userResult.data.user.scimUser); } }}# After handling actions, sync any updated usersbody = await request.json() if request.method in ["POST", "PUT", "PATCH"] else None
result = await auth.scim.scim_request( method=request.method, path_and_query_params=str(request.url.path) + ("?" + str(request.url.query) if request.url.query else ""), body=body, scim_api_key=request.headers.get("authorization"),)
if is_ok(result) and result.data.status == "Completed": # Sync any users that were modified # This isn't necessary, you can call getScimUser on demand as it's pretty fast for user_id in result.data.affected_user_ids: user_result = await auth.scim.get_scim_user( scim_connection_id=result.data.connection_id, user_id=user_id, )
if is_ok(user_result): # Update your database with the latest SCIM data await update_user(user_id, user_result.data.user.scim_user)// After handling actions, sync any updated usersScimRequestResponse result = propelAuthClient.scim.scimRequest( ScimRequestCommand.builder() .method(HttpMethod.valueOf(request.getMethod().toUpperCase())) .pathAndQueryParams(pathAndQueryParams) .body(JsonValue.of(body)) .scimApiKey(request.getHeader("Authorization")) .build());
if (result instanceof ScimRequestResponse.Completed) { ScimRequestResponse.Completed completed = (ScimRequestResponse.Completed) result; // Sync any users that were modified // This isn't necessary, you can call getScimUser on demand as it's pretty fast for (String userId : completed.getAffectedUserIds()) { GetScimUserResponse userResult = propelAuthClient.scim.getScimUser( GetScimUserCommand.builder() .scimConnectionId(completed.getConnectionId()) .userId(userId) .build() );
// Update your database with the latest SCIM data updateUser(userId, userResult.getUser().getScimUser()); }}// After handling actions, sync any updated usersvar result = await propelAuthClient.Scim.ScimRequestAsync(new ScimRequestCommand{ Method = Enum.Parse<HttpMethod>(context.Request.Method, ignoreCase: true), PathAndQueryParams = context.Request.Path + context.Request.QueryString, Body = string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(requestBody) ? null : JsonSerializer.Deserialize<JsonElement>(requestBody), ScimApiKey = context.Request.Headers["Authorization"].ToString(),});
if (result is ScimRequestResponseCompleted completed){ // Sync any users that were modified // This isn't necessary, you can call getScimUser on demand as it's pretty fast foreach (var userId in completed.AffectedUserIds) { var userResult = await propelAuthClient.Scim.GetScimUserAsync(new GetScimUserCommand { ScimConnectionId = completed.ConnectionId, UserId = userId });
// Update your database with the latest SCIM data await UpdateUser(userId, userResult.User.ScimUser); }}Standardizing user data with Mapping Configurations
Section titled “Standardizing user data with Mapping Configurations”Every identity provider sends user data slightly differently - some might include a manager’s email in a custom field, others in an enterprise extension. Rather than handling these variations in your code, you configure the mapping once and PropelAuth BYO handles the translation.
The scim_config file defines which fields you expect, where they can be found in SCIM requests, and how to map them to your user model:
{ "userSchema": [ { // Required. The key for the property in the mapped data. "outputField": "familyName", // Required. The path in the raw SCIM data where this property is expected to be found. "inputPath": "name.familyName", // Optional. If the inputPath is not found, you can specify additional paths to try. "fallbackInputPaths": [ "lastName", // Sometimes customers use "lastName" which isn't standard, but happens "last_name", ], // Required. The type of the property. "propertyType": { "dataType": "String", }, // Optional. A human-readable name for the property -- for example to show to users. "displayName": "Family Name", // Optional. A description of the property. "description": "The user's family name.", // Optional (default false). If true, BYO will surface a warning in the dashboard if this property could not be found in the incoming SCIM data. "warnIfMissing": true, // Optional. A value to return if this property is not found in the incoming SCIM data. // "defaultValue": "Unknown", } ]}The inputPath property defines where in a SCIM request the property can be found. Take this SCIM request, for example:
{ "name": { "givenName": "John", "familyName": "Doe" }, "title": "Manager", "active": true, "emails": [ { "type": "work", "value": "john@acmeinc.com", "primary": true } ], "groups": [], "locale": "en-US", "schemas": ["urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:core:2.0:User"], "userName": "john@acmeinc.com", "externalId": "123123", "displayName": "John Doe", "urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User": { "manager": "jane@acmeinc.com" }, "meta": { "createdAt": "2025-09-15T16:49:20.377943Z", "lastModifiedAt": "2025-09-15T16:49:20.377943Z", "resourceType": "User" }, "id": "315bea4b-390b-4bf4-a6dd-422af2999cfb"}We can see that the user’s last name is located in the familyName property found within the name object. To use this property we can set the input path to name.familyName. If we wanted to get the user’s manager, we would use the input path urn:ietf:params:scim:schemas:extension:enterprise:2.0:User.manager.
This config is a starting point for the information you want to collect from your customer’s IdPs. For more granular control, each SCIM connection can be individually edited in the Dashboard, allowing you to customize the configuration to your customers.
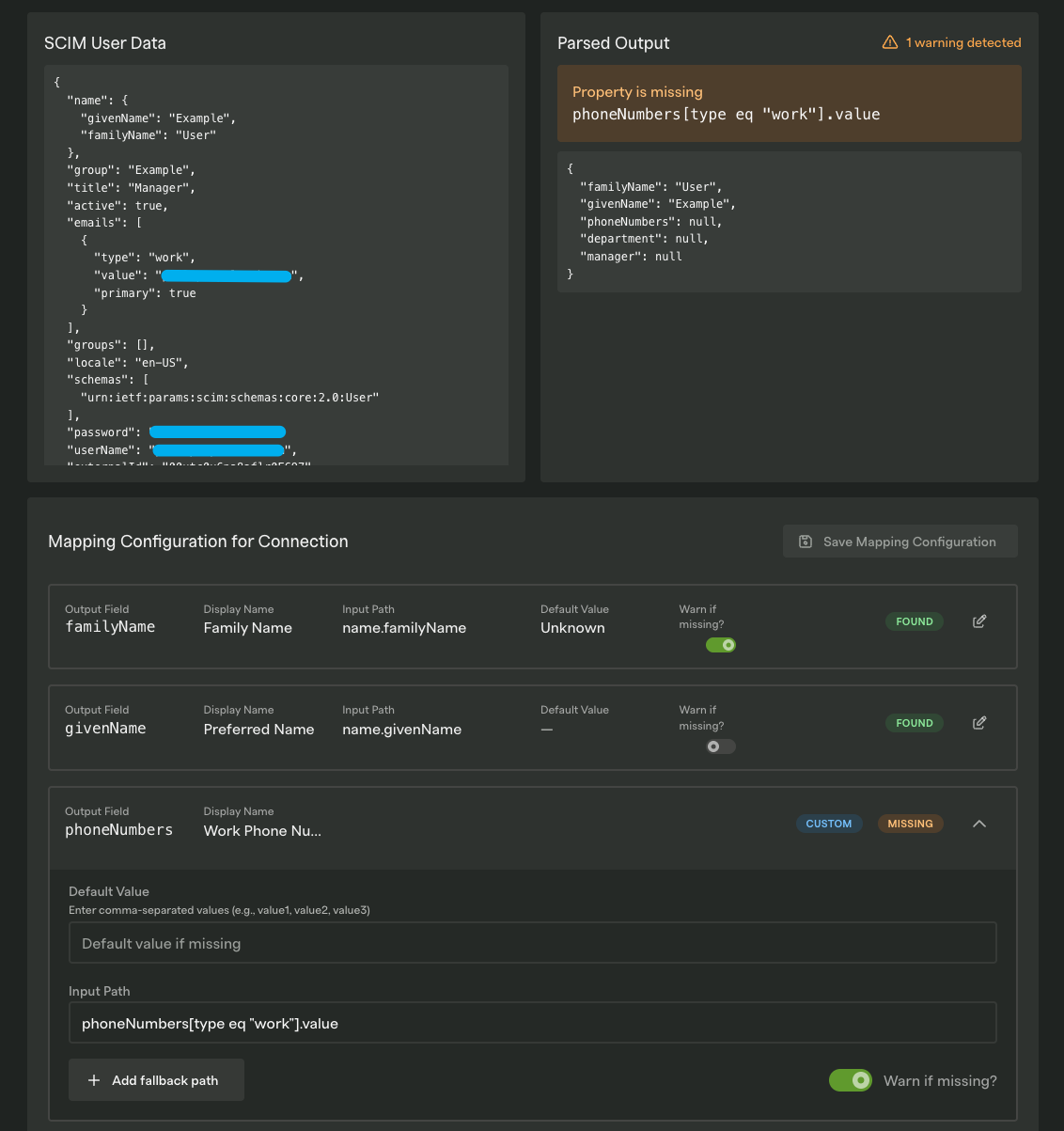
Click here for more information on how to manage SCIM mapping configurations.